CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2020
ABOUT CONFERENCE
With zeal, we are glad to announce the webinar 6th Edition of International Online Conference on Clinical & Medical Oncology (Oncology 2020) organized in collaboration with generous support and cooperation from enthusiastic academicians and Editorial Board Members. Oncology 2020 aims at sharing new ideas and technologies amongst the professionals, industrialists, and students from research areas of Oncology. As the premier event, we have developed a program with your interests in mind. We have not only increased the number of opportunities for you to network with colleagues from across the world but also introduced more focused sessions that will feature cutting-edge presentations, special panel discussions, and livelier interaction with industry leaders and experts.
Oncology 2020 Conference is a novel discussion to unite overall recognized scholastic Researchers, Public wellbeing experts, Scientists, Academic researchers, Industry specialists, Scholars in the field of Oncology, Haematology, Nursing, Radiology, etc., to exchange about the state of the Research and Development.
- Oncologists
- Radiologists
- Chemotherapists
- Cancer Institutes
- Scientists
- Professors
- Doctors
- Medical Colleges
- Medical Practitioners
- Diagnostic Laboratory Professionals
- Students
- Nurses
- Patient Advocates
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Industry professionals
- Marketing, Advertising and Promotion Agency Executives
Why Should Attend??
The arranging group assembles eminent speakers covering the most recent advances in the field, fusing differing qualities in each sense. We likewise incorporate talks on the most recent methodologies for concentrating these biological inquiries.
Exclusive B2B meetings, Interactive Sessions, Panel Discussions, Keynote Sessions, Poster Presentations, Oral Presentations, Workshops, Exhibitions, etc., are the main highlights of this event.
- All accepted abstracts will be published in the supported Journals and Conference Book Proceeding.
- Opportunity to conduct Workshop with your team members
- Networking with Keynote Speakers, OCM, and Eminent personalities for the future course of work.
- Opportunity to chair a session.
- Individual Speaker Page will be created to get more visibility for your scientific research.
- Huge Benefits on Group Registration and much more.
Benefits of WEBINARS:
- International Speaker Certification
- The hard copy of Conference Souvenir, ID card and certificate will be sent to your address
- Online publication of the abstract in the conference website
- Abstract published in the conference
- Proceeding with the unique DOI given
- Exclusive Speaker Pages in relation in conference website for all the speakers
- Publication discount benefits as a conference attendee
- Group Registration discounts
- Outstanding Young Researcher Award
- Nominations for Best Poster Award
- International Networking
- Scientific Association, Collaboration, and more..!
Overview of Oncology and Cancer:
Cancer is an abnormal growth of cells that tend to proliferate in an uncontrolled way, and in some cases, to metastasize/spread. Cancer is not a single or one disease but it is a group of different and distinctive diseases. In all types of cancer, some of the body's cells begin to divide without stopping and spread into surrounding tissues, genetically which are called Oncogenes. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells. As cancer is spreading in the world very rapidly so many market studies and researches are going on and still so many are under study.
The Innovative idea of Cancer has started great much research to be embraced by the labs around the world. With such an extraordinary number of researchers and scientists taking a shot at Caner research, to date, no significant solution for this is recorded. Clinical Oncology at Frankfurt will manage Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of illnesses of the Organ-related Cancers and its inventive strategies. Clinical Oncology will also supply the two days of discussions on methods and systems identified with administration and satisfactory exchange of Cancer and in addition to check out the new thoughts and ideas on worldwide scale and the themes include Cancer Developmental Biology, Clinical Oncology And Medical Case Reports, Oncologic Emergencies In Variety Of Subspecialties, Nucleic Acids Damage, Mutation And Cancer, Cell Signalling And Regulation- Neurology, Cancer Immunology And Immunotherapy, Oncolytic Virus And Cancer, Bioscience- Oncology, Paediatric Oncology, Pharmaceutical Oncology And Pharmacokinetic Studies, Gynaecology, Infectious And Oncology, Key Role Of Pathophysiology In Cancer, Oncology Nursing And Care, Radiology And Imaging Current Technologies, Oncology Chemotherapy Advances Research Studies, Cancer: Complementary & Alternative Treatments, Cancer: LifeStyle Connection, Nutrition & Patient Support, Advances In Cancer Research And Treatment, and Overall Future Outcomes And Change In Oncology Practice.
SESSIONS & TRACKS
Track-1: Cancer Developmental Biology
Cell division could be a traditional method utilized by the body for growth and repair. Healthy cells stop dividing once there's not a requirement for additional female offspring cells; however cancer cells still turn out copies. Cancer cells square measure cells that divide unrelentingly, forming solid tumours or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cancer biology deals with these changes and also the molecular networks that management cell proliferation, differentiation and death. The study of varied styles of cancer is termed as medical specialty.
Track 1-2Regenerative cell biology
Track 1-3Host-pathogen interactions
Track-2: Clinical Oncology and Medical Case Reports
Clinical oncologists are doctors who treat patients with a balance of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. They are involved in the management of all types of cancer and use a range of other treatments to treat cancers, without using surgery.
They are different than medical oncologists, who use non-radiological treatments for cancer. Clinical oncologists determine which treatment to use by considering a range of factors such as the type of tumour, tumour site, the stage of the disease and the patient’s general health. They assess the relative merits of different treatments before presenting these to the patient.
A case study is a research method involving an up-close, in-depth, and detailed examination of a concerned case (subject/topic), as well as its related contextual conditions. Case studies can be produced by a formal research method followed by an individual, organization, event, or action, existing in a specific time and place. Here we are inviting case studies based on any types of cancer or related incidents or events with facts and figures. Presenting your studies on any other type of cancer in this category will privilege you with a 30% discount on registration.
Track 2-2Identifying Risk Factors
Track 2-3Cancer Biologic Factors
Track-3: Oncologic Emergencies in variety of subspecialties
The 3 major specialties of oncology are:
- Medical oncology
- Surgical oncology
- Radiation oncology
There are several sub-specialties in the field of Oncology. The above mentioned specialties deal with the treatment of cancer through Chemotherapy or Immunotherapy, Biopsies and Radiology respectively.

Track 3-6Gastrointestinal oncology
Track 3-7Bone & Musculoskeletal oncology
Track 3-8Dermatological oncology
Track 3-9Genitourinary oncology
Track 3-10Adolescent and young adult (AYA) oncology
Track 3-14Nuclear medicine oncology
Track 3-17Computational Oncology
Track-4: Nucleic acids damage, Mutation and Cancer
DNA is the repository of genetic information in each living cell, its integrity and stability is essential to life. DNA, however, is not inert; rather, it is a chemical entity subject to assault from the environment, and any resulting damage, if not repaired, will lead to mutation and possibly disease.
Track 4-1DNA damage and repair
Track 4-4Induced Mutagenesis in Cancer
Track 4-5Nuclear and Chromatin Dynamics
Track 4-7Circulating Tumour DNA Analysis
Track-5: Cell signalling and regulation- Neurology
In biology, cell signaling is part of any communication process that governs basic activities of cells and coordinates multiple-cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity, as well as normal tissue homeostasis. Errors in signaling interactions and cellular information processing may cause diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding cell signaling, clinicians may treat diseases more effectively and, theoretically, researchers may develop artificial tissues.
All cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings. This is accomplished by a variety of signal molecules that are secreted or expressed on the surface of one cell and bind to a receptor expressed by the other cells, thereby integrating and coordinating the function of the many individual cells that make up organisms. Each cell is programmed to respond to specific extracellular signal molecules. Extracellular signaling usually entails the following steps:
- Synthesis and release of the signaling molecule by the signaling cell.
- Transport of the signal to the target cell.
- Binding of the signal by a specific receptor leading to its activation.
- Initiation of signal-transduction pathways.
Track 5-3Signal transduction in cancer
Track 5-5Cancer: Redox signalling
Track-6: Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy
Cancer immunology is a stream of immunology that studies communications between the immune system and cancer cells (also called tumors or malignancies). It is a field of research that intent to discover cancer immunotherapies to treat and decelerate evolution of the disease. The human immune system mounts natural endogenous response to foreign cells. The gamut of genetics and epigenetics changes occurring in tumors provides diverse set of antigenic repertoire that host’s immune system can exploit to distinguish tumour versus their normal healthy counterparts.
Track 6-1Cancer Antigens & Vaccines
Track 6-3Clinical Cancer immunology
Track 6-4Cellular Immunotherapy
Track-7: Oncolytic Virus And Cancer
An oncolytic virus is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by oncolysis, they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic viruses are thought not only to cause direct destruction of the tumour cells, but also to stimulate host anti-tumour immune system responses. The potential of viruses as anti-cancer agents was first realised in the early twentieth century, although coordinated research efforts did not begin until the 1960s. A number of viruses including adenovirus, reovirus, measles, herpes simplex, Newcastle disease virus, and vaccinia have been clinically tested as oncolytic agents. Most current oncolytic viruses are engineered for tumour selectivity, although there are naturally occurring examples such as reovirus and the senecavirus, resulting in clinical trials.
Track 7-1Oncolytic behaviour of wild-type viruses
Track 7-2Bio-engineered oncolytic virus for the treatment of cancer
Track 7-3Recently approved therapeutic agents
Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment. Nanotechnology as defined by size is naturally very broad, including fields of science as diverse as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, microfabrication, molecular engineering, etc. The associated research and applications are equally diverse, ranging from extensions of conventional device physics to completely new approaches based upon molecular self-assembly, from developing new materials with dimensions on the nanoscale to direct control of matter on the atomic scale.
Track 8-1Cancer Bioinformatics
Track 8-2Cancer Nanotechnology
Track 8-4Cancer & Stem cell technologies
Pediatric Oncology is the term used to comprise all malignant conditions among neonates & children with cancer. The most common childhood cancers are, Neuroblastoma, Retinoblastoma, Wilms tumor and brain tumors, such as gliomas. Childhood cancers are very rare and may differ from adult cancers in the way they grow, spread, treated, and respond to treatment.
Track 9-2Genetics in Paediatric Oncology
Track 9-5Pediatric Oncology Nursing
Track 9-6Integrative Pediatric Oncology
Track 9-7Palliative Care in Pediatric Oncology
Track-10: Pharmaceutical oncology and Pharmacokinetic studies
A multidisciplinary way to deal with redesign has been connected in a variety of settings in clinical oncology, especially among patients with stomach and colorectal malignancy. Cancer has one of the highest mortality rates of all diseases worldwide. As a pre-treatment prior to hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation carried out as a part of treatment for all forms of blood cancer, this drug is contributing to patients as a necessary drug that ranks alongside radiation therapy. Hepatitis B antibody was disease counteractive action antibodies upheld Drug Administration (FDA). Disease treatment immunizations were likewise considered restorative antibodies.
Track 10-1Theoretical Medicines
Track 10-2Anti-Metabolite Drugs
Track 10-5Microtubule Inhibitor
Track-11: Gynaecology, Infectious and oncology
Contaminations in the female genitalia and the extra sex organs are regularly known as Gynecologic InfectiousDiseases. A portion of the irresistible infections is Vulvovaginitis, Cervicitis, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases, and Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Gynecologic Oncology is a specific field that arrangements with growths relating to the female genitalia and conceptive framework.
Track 11-1Oncology Rehabilitation for Cancer
Track 11-2Gynaecologic and Obstetrics Pathology
Track 11-3Polycystic ovary syndrome
Track 11-6Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases
Track 11-7Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Track-12: Key role of pathophysiology in cancer
Pathologists are among the most important members of a patient’s cancer care team. They work to diagnose and determine the stage of cancer, setting the course for what comes next in the treatment journey.Pathology is the service that handles the blood samples and the cells and tissues removed from suspicious ‘lumps and bumps’. Cancer pathology’s key role in diagnosing and treating a complex disease, it’s important to stay up to date on new technologies and breakthroughs that continue to shape the ever-evolving landscape of cancer care.
Track 12-4Anatomical Pathology
Track 12-5Pathology in cancer diagnostics
Track 12-6Cancer Cytopathology
Track-13: Oncology nursing and care
Oncology Nursing is a field including practice incorporates the jobs of direct guardian, instructor, specialist, head, and scientist. Oncology nursing care can defined as meeting the various needs of oncology patients during the time of their disease including appropriate screenings and other preventative practices, symptom management, care to retain as much normal functioning as possible, and supportive measures upon end of life. Cancer Summit 2019 will make another transformation in malignancy science and disease nursing field.

Track 13-3Management & Palliative Care
Track 13-4Assessing Physical & Emotional Status
Track-14: Radiology And Imaging current Technologies
Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose and treat diseases within the bodies of both humans and animals. A variety of imaging techniques such as X-ray radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to diagnose or treat diseases. Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.
Track 14-2Cancer Histopathology
Track 14-3Cancer Differentiation
Track 14-4Computational Oncology
Track-15: Oncology Chemotherapy Advances Research studies
Cancer cells keep growing without control. Chemotherapy is drug therapy for cancer. It works by killing the cancer cells, stopping them from spreading, or slowing their growth. However, it can also harm healthy cells, which causes side effects. Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy and synthetic lethality.
Track 15-1Cancer Radiation Therapy
Track 15-2Cancer Targeted therapy
Track 15-5Cancer Curative treatment
Track 15-6Cancer Palliative treatment
Track 15-7Limitations of Chemotherapy
Track 15-8Cancer Therapeutics, Novel and experimental approaches
Track 15-9Adverse effects of chemotherapy
Track-16: Cancer: Complementary & alternative treatments
Complementary and alternative are terms used to describe many kinds of products, practices, and systems that are not part of mainstream medicine. You may hear them used to refer to methods to help relieve symptoms and improve quality of life during cancer treatment. We call these “complementary” because they are used along with your medical treatment.

Track 16-4Homeopathic Medicines
Track 16-5Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry
Track-17: Cancer: Life style Connection, nutrition & Patient Support
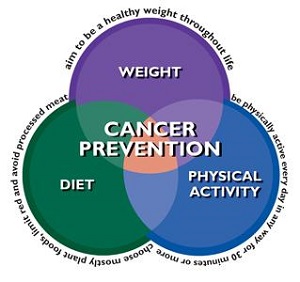
Many factors impact the development of cancer. Over the last 25 years, science has displayed that diet,body weight and physical activity —especially being overweight or obese—are leading risk factors for obtaining certain types of cancer. The main behavioral and environmental risk factors for cancer death in the world are related to diet and physical inactivity, use of addictive substances, sexual and reproductive health and exposure to air pollution and use of contaminated needles.
Track 17-1Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)
Track 17-3Population Attributable Risks
Track-18: Advances In Cancer Research And Treatment
Instruments are designed to aid in the diagnosis, monitoring or treatment of medical conditions. Several new types of equipment are used in the treatment of cancer such as:
Linear Accelerator (LINAC) – It emits radiation of highly localised (X-rays) and it is useful in the treatment of cancer. The 6 MeV linear accelerator having the capability of surface electron allows treating cancer cells even under the subcutis layer overlying the cranium. The patient can also see his activity through the connected display unit.
Gamma Camera – It is used in the detection of cancer via gamma rays. Here tracers used are introduced into the patient’s body intravenously, thus getting the image on the gamma camera as the tracer emits gamma rays which are detected by the gamma camera.
Radiography and Ultrasound – It is a non-invasive way of getting the image of the internal organs by ultrasound. It is a useful method for cancer patients for examining the abdomen for any enlargement of the lymph or masses.
Track 18-1Targeting the DNA Damage Response to Generate New Cancer Therapies
Track 18-2Preclinical & Clinical Research
Track 18-3Early Detection Research
Track-19: Overall Future Outcomes and Change in Oncology Practice
Leukemia, Lymphoma, Germ cell tumors and early stage solid tumors which were once incurable have become curable malignancies now. Immunotherapies have already proven efficient in leukemia, bladder cancer and various skin cancer. For the future, research is promising in the field of physical oncology. Survival of cancer has significantly improved over the past years due to improved screening, diagnostic methods and treatment options with targeted therapy. Large multi-centric Phase III randomised controlled clinical trials by the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast & Bowel Project (NSABP), Medical Research Council (MRC), the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) have contributed significantly to the improvement in survival.
MARKET ANALYSIS
Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation. There are more than 100 types of cancer. The most common causes of cancer death are cancers of Lung (1.69 million deaths), Liver (788 000 deaths), Colorectal (774 000 deaths), Stomach (754 000 deaths) and Breast (571 000 deaths) which accounts for nearly half of new cases per year. Lung cancer, which is highly correlated with cigarette smoking, is responsible for more deaths than any other form of cancer. Cigarette smoking and other environmental factors are associated with the majority of cancers.
The kinds of cancer we expect to increase the most are
- Melanoma (the deadliest kind of skin cancer) in white men and women.
- Prostate, kidney, liver, and bladder cancers in men.
- Lung, breast, uterine, and thyroid cancers in women.
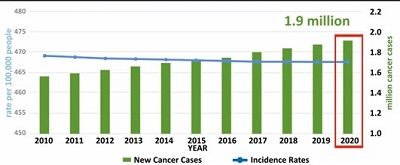
Cancer is among the leading causes of death worldwide. In 2012, there were 14.1 million new cases and 8.2 million cancer-related deaths worldwide. The number of new cancer cases per year is expected to rise to 23.6 million by 2030. The most recent SEER Cancer Statistics Review, released in April 2019, shows that cancer death rates decreased by 1.8% per year among men from 2006 to 2015, 1.4% per year among women from 2006 to 2015 and 1.4% per year among children ages 0–19 from 2011 to 2015.
Global Oncology/Cancer drugs Market is expected to garner $111,938.4 million by 2020, registering a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period 2014 to 2020. Recent progress in biological therapies has widened the scale of therapeutic targets for cancer treatment with the identification of tumour cell specific genes. The number of approved cancer therapies continues to rise. The continued rise and impact of immuno-oncology has been largely centred on the PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors, which have broad efficacy across solid tumours and are used across 23 different tumour types. Overall, the global market for oncology therapeutic medicines will reach as much as $200 billion by 2022, averaging 10—13% growth over the next five years, with the U.S. market reaching as much as $100 billion by 2022, averaging 12–15% growth.
Breakthrough advancements in the development of genetic-based tests for oncology and other disorders during the past few years have significantly propelled market growth. Next generation sequencing technology offers a better understanding of tumor mechanism, thus enabling rational drug design. As a result, more products are expected to get commercialized in the near future.
A rise in oncology-related spending is further expected to fuel market growth in the coming years. Government organizations are focused on encouraging patients to regularly undergo diagnostic examinations to reduce oncology-related healthcare expenditures. As per data estimates, healthcare expenditure is anticipated to rise significantly, thereby influencing the adoption of NGS diagnostics platforms.
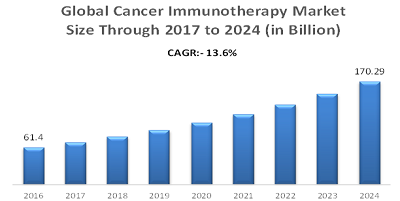
The biotechnology industry is marked by high competition and so is the NGS market for clinical as well as research applications. Prominent participants are actively involved in R&D to develop novel rapid, small, and less expensive platforms. Service providers are embracing the trend of increasing the amount of constructed sequence reads for each cycle run.
Commercially available sequencing platforms analyze both DNA and RNA samples. Key players aim to increase the utility of high throughput technologies for clinical applications. The acquisition of smaller entities operating in the market is also one of the strategic initiatives adopted by players to maintain a competitive position. For instance, in May 2018, Illumina acquired Edico Genome to accelerate data analysis for its next generation sequencing platforms.
LEARN MORE
The age-standardised rate for all cancers (including non-melanoma skin cancer) for men and women combined was 197.9 per 100,000 in 2018. The rate was higher for men (218.6 per 100,000) than women (182.6 per 100,000).
With the burden growing in almost every country, prevention of cancer is one of the most significant public health challenges of the 21st century. Around 40% of cancer cases could be prevented by reducing exposure to cancer risk factors including diet, nutrition and physical activity – for more information see our Cancer Prevention Recommendations or read our blog.
Reducing the cancer burden requires concerted and integrated action from all sectors of society, including civil society, private sector, and health and other professions. You can read what policy actions different countries are taking to promote healthier diets in our NOURISHING framework and accompanying database.
Age-standardised rates are used in the tables. This is a summary measure of the rate of disease that a population would have if it had a standard age structure. Standardisation is necessary when comparing populations that differ with respect to age because age has a powerful influence on the risk of dying from cancer.
- The highest cancer rate for men and women together was in Australia, at 468.0 people per 100,000.
- The age-standardised rate was at least 320 per 100,000 for 12 countries: Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, Hungary, the US, Belgium, France (metropolitan), Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Canada and New Caledonia (France).
- The countries in the top 12 come from Oceania, Europe and North America.
Cancer associations all over the world:
- AIM at Melanoma
- American Brain Tumor Association
- American Cancer Society
- American Childhood Cancer Organization
- American Council on Life Insurers
- American Dietetic Association
- American Hospice Foundation
- American Lung Association
- American Pain Foundation
- American Psychosocial Oncology Society
- American Society of Clinical Oncology
- Angel Flight America
- Association of Oncology Social Work
- Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network
- Bone Marrow & Cancer Foundation
- BreastCancer.org
- Bright Pink
- Cancer Care
- Cancer and Careers
- Cancer
- Cancer Hope Network
- Cancer Legal Resource Center
- Cancer Research and Prevention Foundation
- CaringBridge.org
- CarePages
- Caring Info
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Cancer Information
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
- Center for Mind-Body Medicine
- Children’s Cause for Cancer Advocacy
- Chronic Disease Fund
- Center for Cancer Research
- Clinical Trials
- Colon Cancer Alliance
- Co-Pay Relief Program
- Corporate Angel Network
- CoverageForALL
- Crush It For Curtis Foundation
- Emergingmed
- Facing Our Risk of Cancer EMPOWERED (FORCE)
- Family Caregiver Alliance
- Family Reach
- Feeding America
- Fight Colorectal Cancer
- Head and Neck Cancer Alliance (HNCA)
- Health Resources and Services Administration
- HealthWell Foundation
- Imaginary Friend Society
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer Research Foundation
- Intercultural Cancer Council
- International Myeloma Foundation
- International Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia Foundation
- Joe’s House
- Kidney Cancer Association
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
- Living Beyond Breast Cancer
- Lung Cancer Alliance
- LUNG evity Foundation
- Lymphoma Research Foundation
- Melanoma Research Foundation
- Men Against Breast Cancer
- MetaCancer Foundation, Inc.
- Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation
- Mylifeline.org
- National Brain Tumor Society
- National Breast Cancer Coalition
- National Cancer Institute
- National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- National Cervical Cancer Coalition
- National Children’s Cancer Society
- National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship
- National Energy Assistance Referral
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization
- National Lymphedema Network
- National Marrow Donor Program
- National Organization for Rare Disorders
- National Ovarian Cancer Coalition
- National Patient Travel Center
- Native American Cancer Research
- NeedyMeds
- Nueva Vida
- Office of Minority Health
- Oncolink
- Oncology Nursing Society
- Oral Cancer Foundation
- Ovarian Cancer National Alliance
- Pancreatic Cancer Action Network
- Partnership for Prescription Assistance
- Patient Access Network Foundation
- Patient Advocate Foundation
- Patient Services, Inc. (PSI)
- Prostate Cancer Foundation
- The Prostate Net
- Rosalynn Carter Institute for Caregiving
- Sisters Network
- Skin Cancer Foundation
- Social Security Administration
- State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIP)
- Survivorship A to Z
- Support for People with Oral and Head and Neck Cancer (SPOHNC)
- Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation
- Thyroid Cancer Survivor’s Association
- Together Rx Access
- The Ulman Cancer Fund for Young Adults
- United Way
- Uniting Against Lung Cancer
- US TOO International Prostate Cancer Education & Support Network
- Vital Options International
- WomanLab
- Young Survival Coalition
- Zero - The Project to End Prostate Cancer
List of Cancer Hospitals all over the world:
- Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center
- Antoni van Leeuwenhoekziekenhuis
- Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR
- City of Hope National Medical Center
- Cross Cancer Institute
- Dharamshila Cancer Hospital and Research Centre
- Docrates Cancer Center
- Dr. B. Borooah Cancer Institute
- Finsen Laboratory
- Fox Chase Cancer Center
- Fuda Cancer Hospital-Guangzhou
- Homi Bhabha Cancer Hospital & Research Centre
- Huntsman Cancer Institute
- Institute of Cancer of São Paulo
- Integris Cancer Institute
- The James Cancer Hospital
- John Stoddard Cancer Center
- Kanagawa Cancer Center
- Kidwai Memorial Institute of Oncology
- King Hussein Cancer Center
- Mahavir Cancer Institute and Research Centre
- Malabar Cancer Centre
- Mary Bird Perkins Cancer Center
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute
- National Institute of Cancer Research and Hospital
- New York Cancer Hospital
- Oncocare
- Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
- Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
- Radiumhemmet
- Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre
- Reno CyberKnife
- Royal Marsden HospitalSeton Healthcare Family
- Shanghai Cancer Center
- Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center
- Tata Memorial Centre
- Tom Baker Cancer Centre
- UCSF Bakar Cancer Hospital
- UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center
- University of Florida Cancer Hospital
- University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center
- University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
- Vattikuti Urology Institute
- Velindre Cancer Centre
- Victorian Comprehensive Cancer Centre
- Winship Cancer Institute
- Zhejiang Cancer Hospital
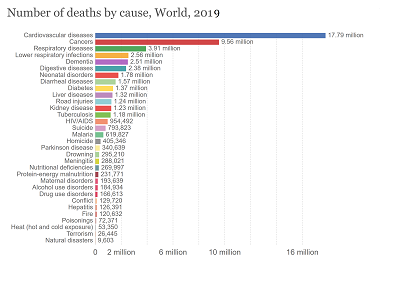
No. of deaths caused by cancer, World 2019 statistics:
Cancer is a generic term for a large group of diseases that can affect any part of the body. Other terms used are malignant tumours and neoplasms. One defining feature of cancer is the rapid creation of abnormal cells that grow beyond their usual boundaries, and which can then invade adjoining parts of the body and spread to other organs, the latter process is referred to as metastasizing. Metastases are a major cause of death from cancer.
- Cancer is the second leading cause of death globally, and is responsible for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018. Globally, about 1 in 6 deaths is due to cancer.
- Approximately 70% of deaths from cancer occur in low- and middle-income countries.
- Around one third of deaths from cancer are due to the 5 leading behavioural and dietary risks: high body mass index, low fruit and vegetable intake, lack of physical activity, tobacco use, and alcohol use.
- Tobacco use is the most important risk factor for cancer and is responsible for approximately 22% of cancer deaths.
- Cancer causing infections, such as hepatitis and human papilloma virus (HPV), are responsible for up to 25% of cancer cases in low- and middle-income countries.
- Late-stage presentation and inaccessible diagnosis and treatment are common. In 2017, only 26% of low-income countries reported having pathology services generally available in the public sector. More than 90% of high-income countries reported treatment services are available compared to less than 30% of low-income countries.
- The economic impact of cancer is significant and is increasing. The total annual economic cost of cancer in 2010 was estimated at approximately US$ 1.16 trillion.
- Only 1 in 5 low- and middle-income countries have the necessary data to drive cancer policy.
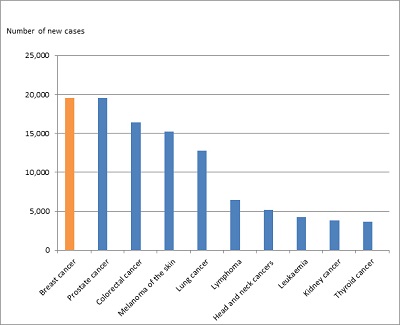
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2019. The most common cancers are:
- Lung (2.09 million cases)
- Breast (2.09 million cases)
- Colorectal (1.80 million cases)
- Prostate (1.28 million cases)
- Skin cancer (non-melanoma) (1.04 million cases)
- Stomach (1.03 million cases)
The most common causes of cancer death are cancers of:
- Lung (1.76 million deaths)
- Colorectal (862 000 deaths)
- Stomach (783 000 deaths)
- Liver (782 000 deaths)
- Breast (627 000 deaths)
World Wide Cancer Universities
List of Cancer University in USA:
- Stanford University
- Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
- UCSF School of Medicine
- Duke University
- Yale School of Medicine
- Harvard Medical School
- UNC School of Medicine
- UT South western Medical School
- The University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine
- Maryland School of Medicine
- University of Cincinnati Academic Health Centre
- University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
- University of Minnesota Medical School
- Stony Brook School of Medicine
- Vermont College of Medicine
- International Medical Conferences
- International Medical Conferences
- Wayne State School of Medicine
- Emory University: School of Medicine
- University of Utah School of Medicine
- Vanderbilt University
- Penn State Hershey College of Medicine
- Alabama School of Medicine
- UMASS School of Medicine
- Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
- Oklahoma College of Medicine
- Clinical Oncology Conferences
List of Cancer University in Europe:
- ESO - European School of Oncology
- Kharkiv National Medical University
- Cardio-Oncology Conferences
- Medical University – Plovdiv
- Medical University – Pleven
- Bukovinian State Medical University
- KU Leuven – University of Leuven, Belgium
- Technical University of Munich
- Humboldt University of Berlin
- University of Amsterdam
- Erasmus University Rotterdam
- Leiden University
- RWTH Aachen University
- University of Groningen
- Utrecht University
- University of Tübingen
- Yerevan State Medical University
- University of Copenhagen
- Maastricht University
- Medical University of Vienna
- University of Milan
- University of Barcelona
List of Cancer University in Asia:
- University of Tokyo
- National University of Singapore
- Kyoto University
- University of Hong Kong
- Peking University
- Seoul University
- National Taiwan University
- Osaka University
- Tsinghua University
- Duke-NUS Medical School
- Asian Medical Institute
- International Medical University
- Taipei Medical University
- Allianze University College of Medical Sciences
- Mahidol University
- Herat University Faculty of Medicine
- Karaganda State Medical University
- Perdana University Graduate School of Medicine
- Chongjin Medical University
- Nanyang Technological University
List of Cancer University in Africa:
- Makerere University
- University of Ghana at Legon
- University of Nairobi
- University of Ibadan
- University of Botswana
- University of Lagos
- Cheikh Anta Diop University
- University of Dar Es Salaam
- University of Cape Town
- Stellenbosch University University of Pretoria
- Cairo University
- University of Witwatersrand
- University of Kwazulu-Natal
- University of Western Cape
- Mansoura University
- University of Johanessburg
- Orotta School of Medicine
- Addis Ababa University
- Aga Khan University Medical School
- Egerton University Medical School
- University of Malawi College of Medicine
- Ambrose Alli University
- Walter Sisulu University
- Busitema University School of Medicine
World Wide Oncology and Cancer Based Companies
List of Oncology and Cancer based Companies in the USA:
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- AMGN
- Biogen, Inc.
- Celgene Corporation
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Illumina
- BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Flatiron Health
- Epizyme
- ARMO BioSciences
- Guardant Health
- Tesaro
- Mersana Therapeutics
- CytomX Therapeutics
- Edico Genome
- Raze Therapeutics
- G1 Therapeutics
- Agenus Inc.
- Personal Genome Diagnostics (PGD)
- VentiRx Pharmaceuticals
List of Oncology and Cancer Based Companies in Europe:
- Sanera Pharmaceuticals
- Aromics
- Kuzey Pharma
- Remedica Ltd
- Azanta
- Bone Therapeutics
- Iteos Therapeutics
- Regenesys (Athersys)
- Linatech
- Dandrit Biotechnology
- Dako (Agilent)
- H-Immune
- Pierre Fabre
- Oncodesign
- Anagenesis Biotechnologies
- Aratinga Bio
- Genclis
- Vaxon Biotech
List of Oncology and Cancer Based Companies in Asia:
- Shionogi Pharmaceutical Research Facility
- Taiyo Pharmaceutical Industry
- WuXi Biologics’ Perfusion Biologics
- Nippon Shinyaku Corporation
- Medlac Pharmaceutical Plant
- Lonza Niacinamide Production Facility
- Kemwell Biopharmaceuticals Inc.
- Hanmi Pharmaceutical's New Bio Manufacturing Plant
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- WuXi Biologics’ Perfusion Biologics
- Pfizer’s Global Biotechnology Centre
- GlaxoSmith Kline’s (GSK) Pharmaceutical Inc.
- Affymetrix Inc
- Daiichi Pharmaceutical Company
- Merck Serono’s Pharmaceuticals
- Novartis Institute of BioMedical Research
- Searle Pharma Medication Production Plant
- GE Healthcare Shanghai Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plant
- AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plant
List of Oncology and Cancer Based Companies in Africa:
- Enaleni Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Amalgamated Pharmaceuticals
- Dibana Pharmaceuticals
- Abbott Laboratories SA
- Teva Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Amka Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Medimoc Sarl
- AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Lilly Oncology - Lilly South Africa
- Warren Chem Pharmaceuticals
- Biotech Laboratories Ltd
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- Axim Pharmaceuticals
- Keko PharmaceuticalIndustries Ltd
- Pharmed Pharmaceuticals
- Embassy Pharmaceuticals
- S D V Pharmaceuticals
- Georen Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Allied Drug Company Ltd
World Wide Cancer Journals
List of Cancer Journals in USA:
- Cancer Cell
- Journal of Clinical Oncology
- Journal of the National Cancer Institute
- Stem Cells
- Cancer
- Molecular Cancer Therapeutics
- International Journal of Radial Oncology Biology Physics
- Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
- Advances in Cancer Research
- Oncotarget
- Journal of Cancer Survivorship
- Cancer Prevention Research
- Journals of Thoracic Oncology
- Current Opinion in Oncology
- Cancer Control
- Cancer Cytopathology
List of Cancer Journals in in Europe:
- Lancet Oncology
- Drug Resistance Updates
- Breast Cancer Research
- European Journal of Cancer
- Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology
- British Journal of Cancer
- Blood Reviews
- Molecular Cancer
- Endocrine-Related Cancer
- Psycho-Oncology
- Pigment Cell and Melanoma Research
- Cancer Science
- Environmental Carcinogenesis and Ecotoxicology Reviews
- Journal of Hematology and Oncology
List of Cancer Journals in Asia:
- Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention
- Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention
- The Japanese Association of Medical Sciences
- Angiogenesis in Multiple Myeloma: Implications in Myeloma Therapy
- Lymphoma in Asia
- Arsenates in the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies
- Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment for Early Gastric Cancer
- Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health
- Liver Cancer
List of Cancer Journals in Africa: